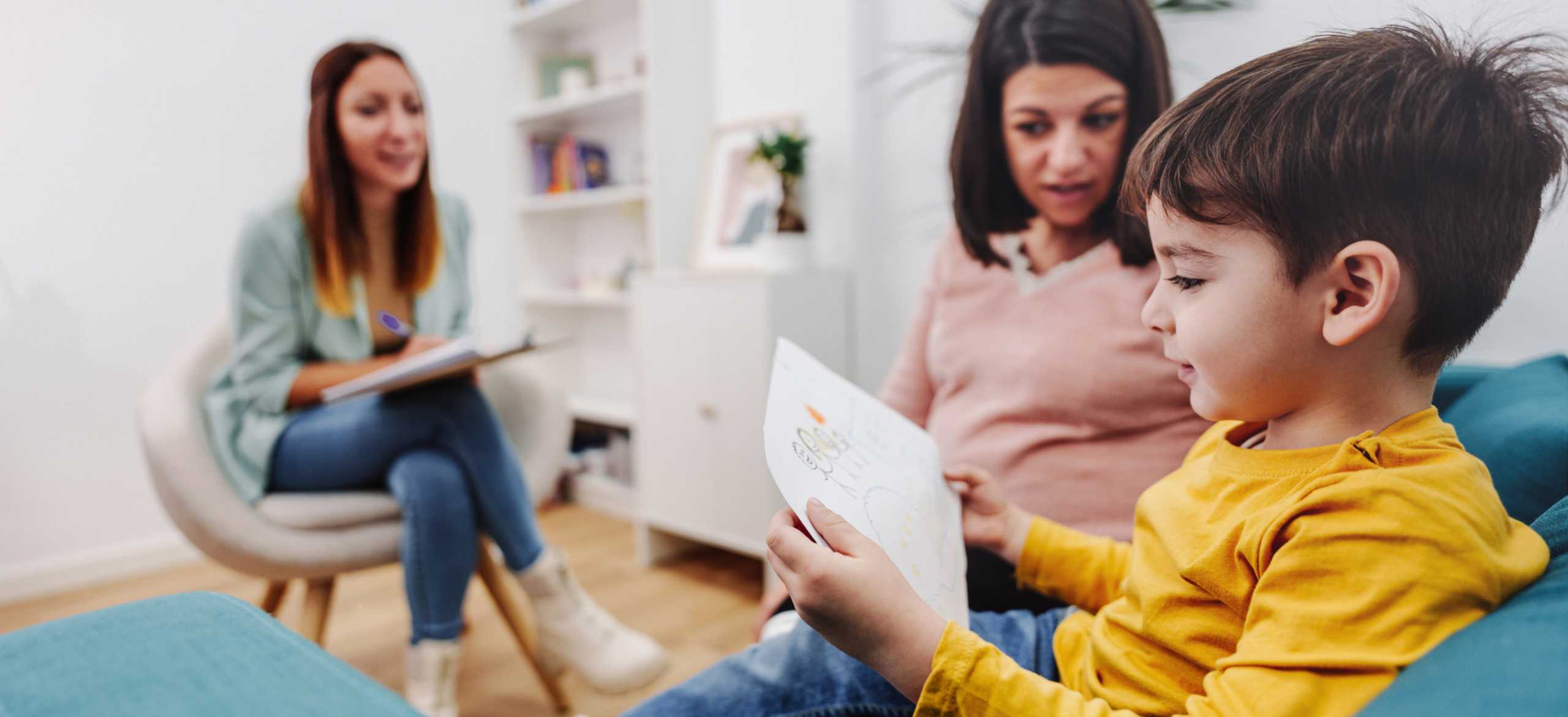
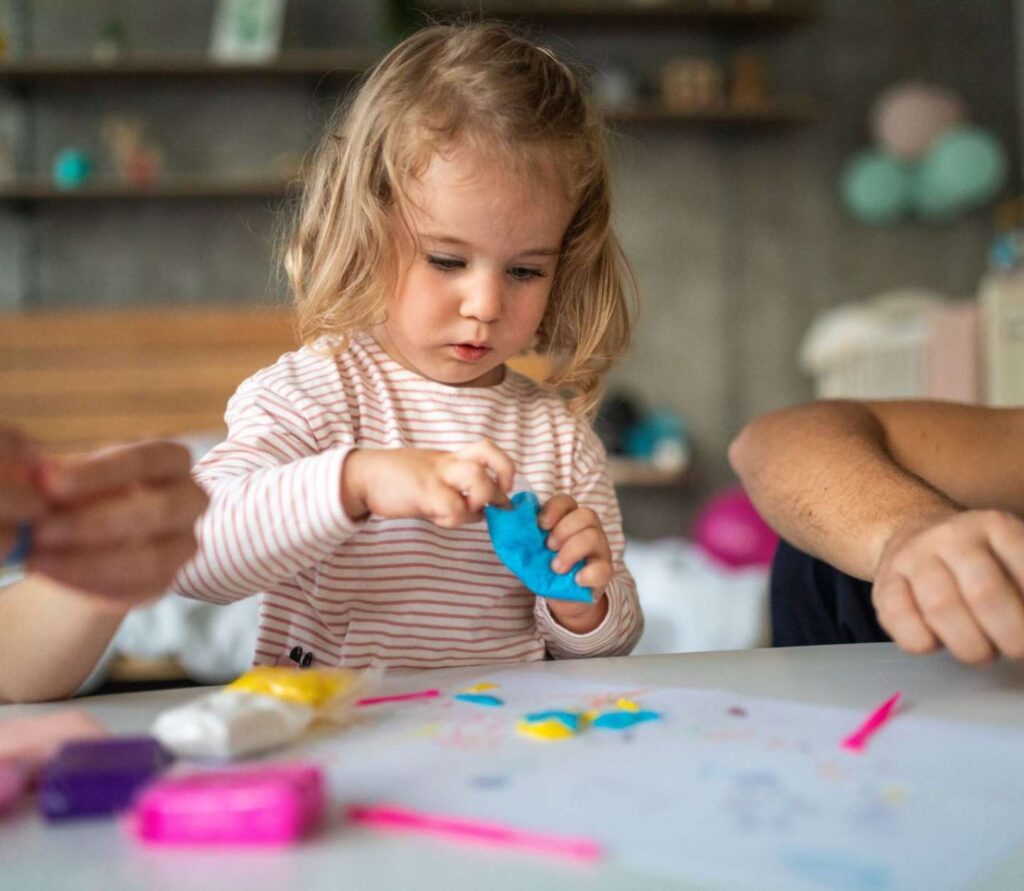
Every child with autism has different needs, and any therapy will be an individualised approach to address them.
There are evidence-based pathways in early intervention, such as ABA or ESDM. And common approaches that help are Psychology, Occupational Therapy, Speech Pathology and behaviour therapists.
There are many different approaches for the treatment of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), but there are a few general categories, and chances are your child will receive a combination.
Behavioural
Behavioural approaches focus on changing behaviours by understanding what happens before and after the behaviour.
Developmental
Developmental approaches focus on improving specific developmental skills, such as language skills or physical skills.
Educational
Educational treatments are given in a classroom setting, with teachers adjusting the classroom structure to improve academic and other outcomes.
Social-relational
Social-relational treatments focus on improving social skills and social interaction, and building emotional bonds and can involve parents or peer mentors.
Pharmacological
Some medications treat symptoms that can help people function better. For example, to manage high energy levels, inability to focus, or self-harming behaviour, as well as co-occurring psychological conditions, such as anxiety or depression.
Psychological
Psychological approaches can help people with ASD cope with anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. For example, Cognitive-Behaviour Therapy (CBT) can change how the person thinks about a situation to change how they react to it.
Complementary and alternative
Some treatments are used to supplement more traditional approaches, such as special diets, herbal supplements, chiropractic care, animal therapy, art therapy, mindfulness, or relaxation therapies.